Auxiliaries for the FRP Industry
In the FRP (Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic) industry, several auxiliary materials, aside from resins and gelcoats, are crucial for ensuring optimal production and performance. Curing agents (hardeners) are used to initiate the chemical reaction that solidifies the resin, ensuring strength and durability in the final product. Fiberglass mats (CSM) and fiberglass roving serve as reinforcement materials, providing the composite with the necessary strength and structural integrity. Fiberglass cloth is also commonly used for specific laminating needs, offering a smooth finish and additional reinforcement. Release agents are applied to molds to prevent the FRP products from sticking during the curing process, making demolding easy. Accelerators speed up the curing time, improving efficiency, while thixotropic agents adjust resin viscosity, ensuring better application, particularly on vertical or intricate surfaces. Pigments and colorants are added to resins and gelcoats to achieve desired colors, finishes, and UV protection. Fillers are incorporated to enhance mechanical properties or reduce material costs. Additionally, brushes are essential tools for applying resins and gelcoats to surfaces with precision. Polyester film is sometimes used as a backing material in composite manufacturing, offering support during molding. Lastly, fire retardants are added for applications requiring flame resistance. These auxiliaries work together to ensure that FRP products meet stringent performance, durability, and aesthetic requirements.



FIBERGLASS CHOPPED STRAND MAT
Composed of randomly oriented glass fibre held together by a binder, Chopped Strand Mat provides strength and stiffness to composite structures while allowing for conformability to complex shapes. During fabrication, CSM is typically impregnated with resin and then laid up in layers to form the desired shape. 100, 150,180, 225, 300, 450,600, 900 in powder and emulsion
GLASS FIBER WOVEN FABRIC
Composed of woven strands of glass fibres, this fabric offers excellent mechanical properties, including tensile strength, stiffness, and resistance to impact and abrasion. composite manufacturing, glass fibre woven fabric is typically impregnated with resin, such as epoxy or polyester, to create a composite material with enhanced properties. This process, known as wet layup or vacuum bagging, allows for the fabrication of lightweight and high-strength components used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, marine, construction, and sports equipment. 400, 610,800,1000,1200
E GLASSFIBER DIRECT ROWING
E-glass roving mat, is a type of reinforcement material used in composite manufacturing processes. It is made from continuous strands of E-glass fibres arranged randomly and bonded together with a binder. E-glass fibre roving mat is valued for its high strength, durability, and versatility in a wide range of composite applications. 1200, 2400, 4800
FIBERGLASS COMBINATION MAT
This combination of materials offers the benefits of both chopped strand mat and woven roving fabric, providing excellent strength, stiffness, and impact resistance. The chopped strand mat provides uniform distribution of fibres in multiple directions, while the woven roving fabric adds additional strength and stability along the length and width of the composite laminate. 600, 900
FIBERGLASS MESH
Fiberglass mesh is a vital component in the FRP (Fiber Reinforced Plastics) industry, serving primarily as reinforcement in composite materials. It enhances strength, stiffness, and impact resistance of FRP products such as laminates, panels, pipes, and structural components. Fiberglass mesh is used in mold making for maintaining shape accuracy, offers corrosion resistance, and supports versatile design possibilities. Its lightweight nature reduces overall weight in applications while ensuring durability in diverse industries including construction, automotive, aerospace, and marine sectors. 45,80 GSM
COBALT OCTOATE
3%, 6%: Cobalt octoate is commonly used as an accelerator in the curing process of unsaturated polyester resins, which are the most widely used resins in FRP manufacturing. It accelerates the cross-linking reaction between the resin and the curing agent (typically a peroxide), speeding up the curing process and reducing gel time.
COLOURLESS COBALT
Colourless cobalt compounds are preferred in FRP manufacturing because they do not impart any colour to the resin, allowing for the production of transparent or light-coloured composite parts. This is particularly important in applications where aesthetics are a consideration, such as in the production of clear panels, translucent surfaces, or coloured composite products where pigment dispersion is crucial.
HARDNER/CATALYST
The hardener or catalyst initiates the chemical reaction between the resin and the curing agent (often a peroxide), which leads to the formation of cross-links between the polymer chains. This process, known as curing or polymerization, transforms the liquid resin into a solid, durable material.
STYRENE MONOMER
Styrene monomer is the primary solvent cum monomer used in the polymerization process of unsaturated polyester resins (UPR). When combined with other ingredients such as organic peroxides and/or cobalt based accelerator, styrene undergoes a chemical reaction to form a thermosetting polymer matrix. This matrix binds the fiberglass reinforcement together, imparting strength and rigidity to the composite material. Mylar/Polyester Film: polyester film serves multiple purposes in the FRP industry, providing essential functionality in moulding, vacuum bagging, surface protection, and finishing processes. Its versatility, durability, and compatibility with resin systems make it a valuable material for manufacturers seeking efficient and reliable solutions for composite fabrication.
POLYESTER CLOTH
In the FRP industry, polyester cloth is often combined with resins to create strong and lightweight composite structures. It can be woven in different patterns and weights, allowing for customization based on specific performance requirements. The cloth's compatibility with various resin systems, including unsaturated polyester and vinyl ester resins, further enhances its utility.
OTHER AUXILIARIES
- Silica Powder
- Aerosil Powder
- Calcium Carbonate Powder
- Titanium Dioxide Powder
- Pigments
- Aluminium Roller
- Brushes
- Agro-shade Net
- Rubber Solution
- Wax Solution
- ATH (Aluminium Tri Hydrate)
- Powder
- PVA Liquid/Powder
- PUF (Polyurethane Foam)-
- Polyol and Hardner
- Acetone
- Mold Release Agent
Auxiliaries Products Range

Curing Agents (Hardeners)
Our Curing Agents are designed for efficient crosslinking, ensuring optimal curing of resins and superior mechanical properties in the final composite.

Catalysts
Catalysts help control the polymerization process, ensuring that the resin reacts properly and the final product achieves the desired properties.

Pigments & Fillers
We provide a wide selection of Pigments and Fillers to enhance color, texture, and mechanical strength of your composites.
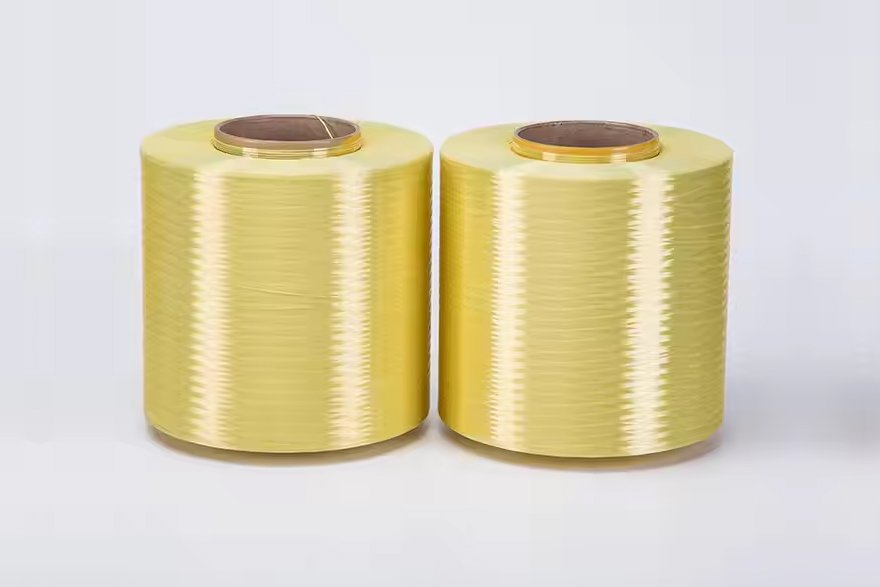

Reinforcements
High-performance Fibers and Reinforcements—including glass, carbon, and aramid fibers—are available to improve strength, stiffness, and impact resistance.
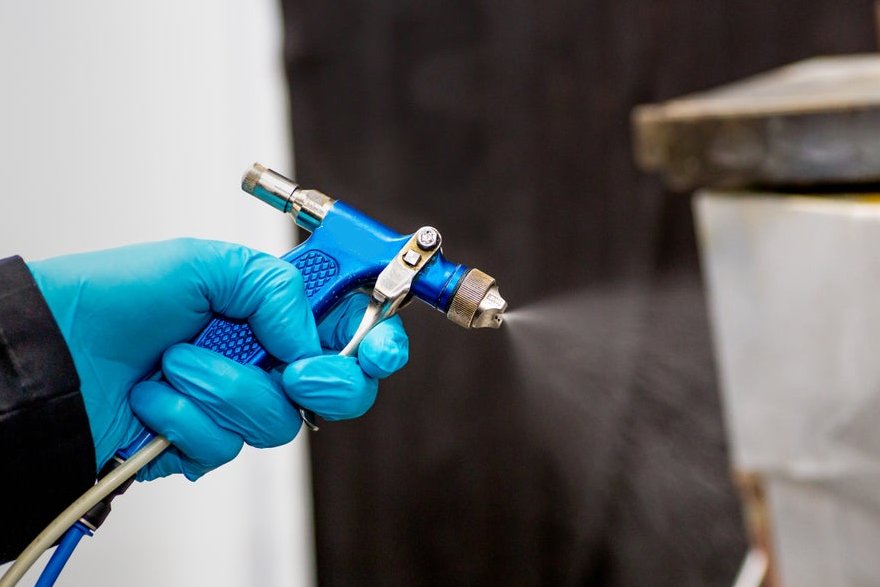

Release Agents
Release Agents ensure easy removal of FRP components from molds while improving surface finishes.
Adhesives and Bonding Agents
Our Adhesives and Bonding Agents provide strong, long-lasting adhesion for composite materials, ensuring the integrity of your products.